In many industrial and mechanical systems, insufficient lubrication leads to premature bearing wear, downtime, and high maintenance costs. Yet many engineers and maintenance teams overlook one simple but critical factor — the type of grease fitting used. Without the right fitting, grease cannot reach friction points efficiently, resulting in wasted lubricant and equipment failure. Selecting the proper grease fitting for each application ensures precise lubrication, contamination prevention, and long-term reliability — the very focus of this article.
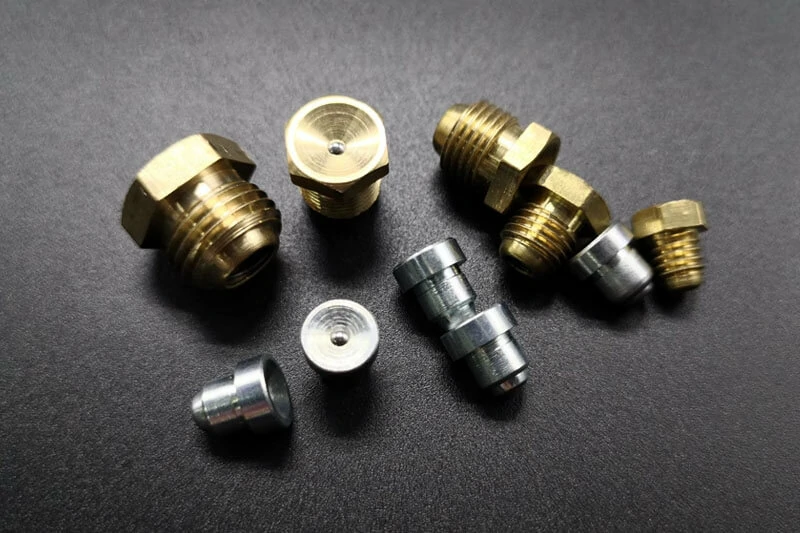

A grease fitting is a small mechanical component that allows grease to be injected into a machine part under pressure while preventing contaminants from entering. Common types include straight, angled (45°/90°), button head, flush-type, drive-type (push-in), and remote fittings, each serving specific lubrication and accessibility needs.
Curious which type fits your equipment best? Let’s explore how each grease fitting works, where it’s used, and what makes it essential for efficient industrial maintenance.
What Are the Different Types of Grease Fittings and Their Functions?
Straight Grease Fittings
Straight grease fittings — often called standard or Zerk fittings — are the most widely used type across industrial machinery. They feature a threaded body with a ball-check valve that opens under grease gun pressure and seals afterward to block contaminants.
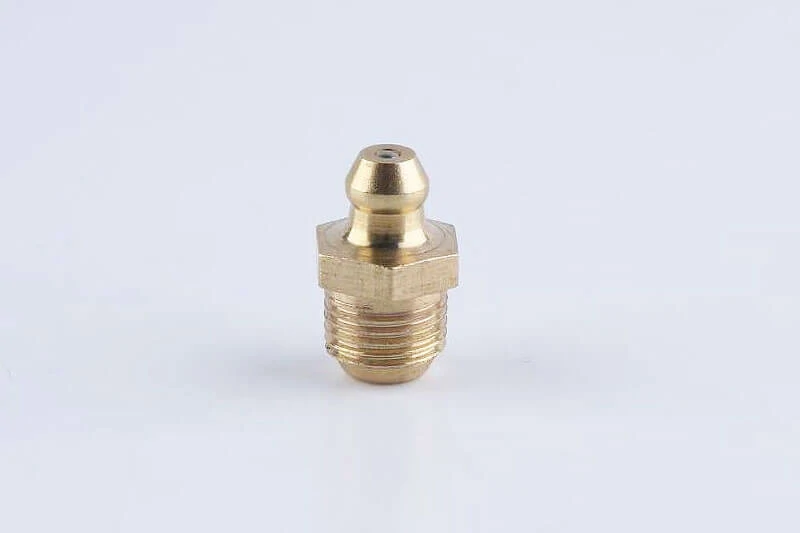

Function:Their main purpose is to deliver grease directly into bearings, bushings, or pivot points. The internal check valve prevents dirt or debris from entering the system once lubrication is complete.
Applications:General industrial machinery、Pumps and compressors、Bearings and couplings with direct line access
Advantages:Simple to install and maintain、Universally compatible with most grease guns、Available in multiple thread sizes and materials
Limitations:Requires direct, straight-on access — unsuitable for confined or angled areas
Example:In an instrumentation valve manifold, straight fittings can be installed on easily accessible ports to facilitate quick lubrication during scheduled maintenance cycles.
Angled Grease Fittings (45° and 90°)
When access is limited, angled fittings solve the problem. These fittings feature the same check-valve design but are bent at a 45° or 90° angle to reach lubrication points that are obstructed or located in tight spaces.
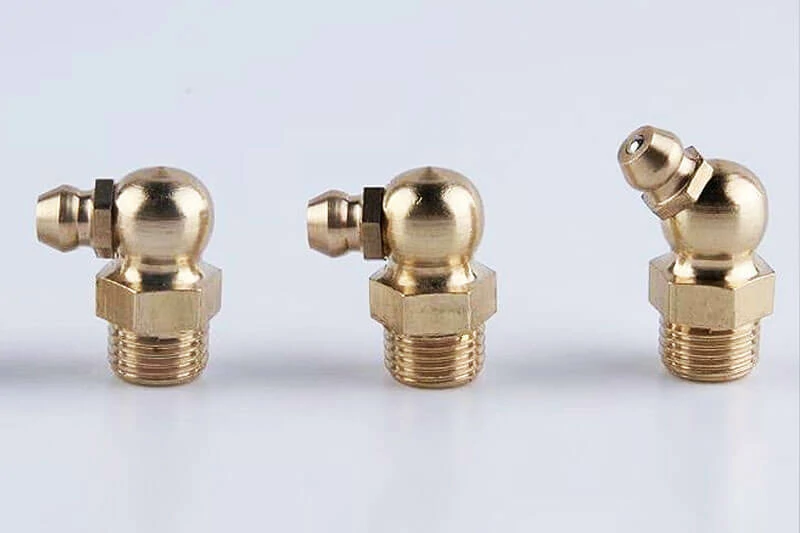

Function:They allow technicians to apply grease from the side, ensuring full coverage even when a direct line of sight or approach is impossible.
Applications:Tight or recessed lubrication points、Inside enclosed frames or machinery housings、Valve assemblies with complex geometries
Advantages:Enables lubrication in difficult-to-reach locations、Reduces downtime by eliminating the need for disassembly、Available in various thread types (metric, SAE, BSP)
Limitations:Slightly reduced grease flow efficiency due to the bend,Must ensure proper alignment between grease gun coupler and fitting angle
Example:A 90° grease fitting is ideal for greasing valve stems located behind control panels, where space prevents a straight gun approach.
Button-Head Grease Fittings
Button-head fittings are easily recognizable by their wide, flat heads designed for high-volume lubrication. They are commonly used in heavy machinery, construction, and mining equipment.
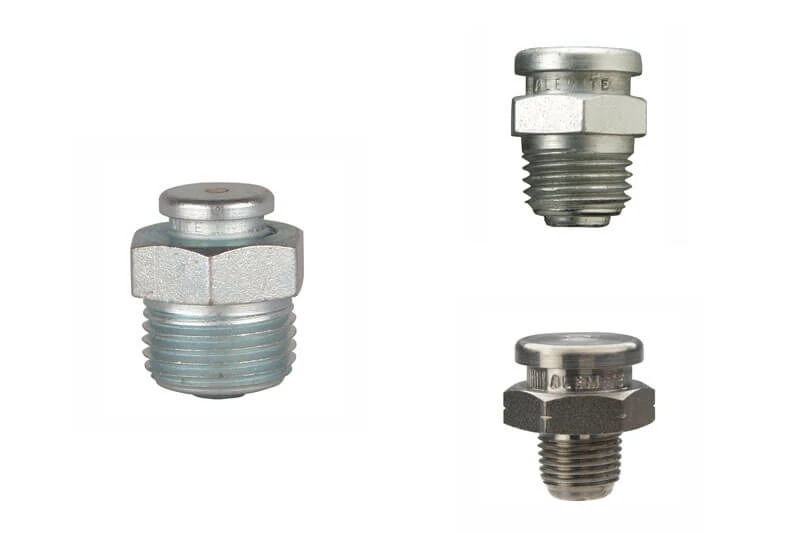

Function:These fittings allow quick connection to a specialized grease coupler, enabling large quantities of grease to be delivered rapidly into oversized bearings or sliding components.
Applications:Heavy-duty machinery (cranes, loaders, excavators)、Large bearing housings and couplings、Industrial and marine valve assemblies
Advantages:Handles higher grease flow rates、More robust connection for pressurized systems、Resistant to accidental damage or disconnection
Limitations:Requires a special button-head coupler、Bulkier head design may limit installation in compact areas
Example:For high-pressure valve actuators, button-head fittings ensure continuous lubrication without the risk of blowout or leakage under extreme loads.
Flush-Type Grease Fittings
Flush-type fittings are designed to sit level with or below the surrounding surface. They are used in applications where protruding fittings could be damaged by moving parts or pose a safety hazard.
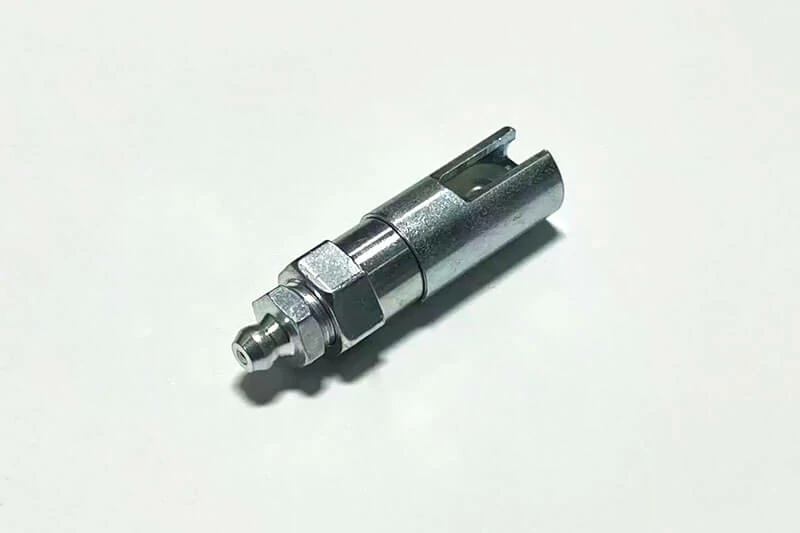

Function:They provide a discreet entry point for lubrication while preventing grease nipples from snagging or shearing off during operation.
Applications:Rotating equipment (shafts, couplings, flywheels)、Aerospace and automotive assemblies、Sliding mechanisms or pivot arms with minimal clearance
Advantages:Minimizes exposure to damage and contamination、Ideal for compact or safety-critical designs、Maintains smooth exterior surfaces
Limitations:Requires a special grease gun tip or needle nozzle,More difficult to locate visually during maintenance
Example:Flush fittings are perfect for valve handles or levers where a projecting nipple could interfere with rotation or user handling.
Drive-Type (Push-In) Grease Fittings
Drive-type fittings, also known as push-in fittings, feature a smooth or barbed shank that can be hammered or pressed into a hole without threads.
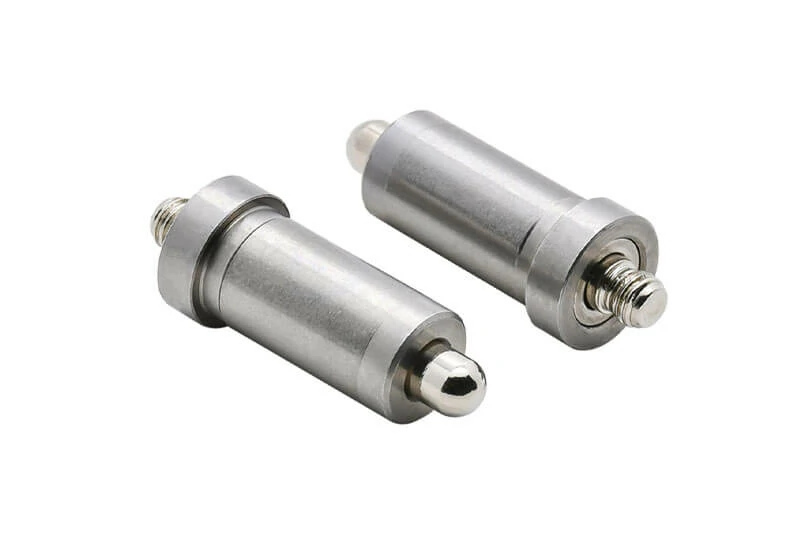

Function:They provide a quick, secure lubrication point in applications where threading is unnecessary or impractical.
Applications:Sheet metal components、Cast housings or aluminum parts、Retrofit or repair jobs where re-tapping is not viable
Advantages:Fast installation without tapping threads、Reduces maintenance time
Available for both low and medium-pressure lubrication systems
Limitations:Less secure than threaded fittings in high-pressure systems,Removal can damage the surrounding bore if not handled carefully
Example:In mass-produced valve components where cost and speed matter, drive-type fittings simplify installation and eliminate machining threads in softer materials.
Remote or Extended Grease Fittings
Remote grease fittings extend access to hard-to-reach lubrication points using hoses, tubing, or manifolds that relocate the grease nipple to an easily accessible spot.
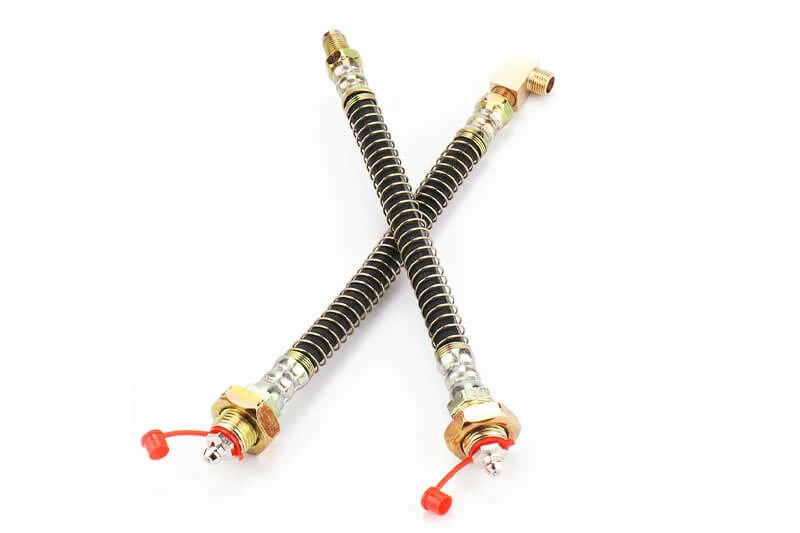

Function:They allow operators to lubricate internal or hazardous components safely from outside the equipment.
Applications:Enclosed or shielded valve manifolds、Machinery with multiple lubrication points、Equipment requiring centralized greasing systems。
Advantages:Improves maintenance safety and accessibility、Reduces downtime for large or complex machines、Supports multiple fittings via manifold blocks。
Limitations:Requires additional hoses and connectors、Must be installed carefully to prevent leaks or line blockages
Example:For high-pressure double block & bleed valves, remote grease fittings can centralize lubrication lines so maintenance crews can grease both valve seats from a single external access point.
What Are the Common Materials and Thread Standards for Grease Fittings?
Grease fittings are available in a variety of materials and thread types, depending on environmental and mechanical requirements.

Common materials
- Steel: Standard option for general use.
- Stainless steel: Corrosion-resistant; suitable for marine and chemical industries.
- Brass: Soft metal, used in low-pressure or nonferrous assemblies to prevent galling.
Thread standards
- SAE-LT (Society of Automotive Engineers – Lubrication Thread): 1/4-28 UNF thread commonly used in North America.
- NPT (National Pipe Thread): 1/8″ NPT for heavier industrial use.
- Metric Threads: M6×1, M8×1, M10×1 types for international equipment.
- BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper): Common in Europe and Asia.
For global exporters like WalterValves, maintaining both metric and imperial stock ensures compatibility across markets such as the U.S., Europe, and Southeast Asia.
Why Are Grease Fittings Important in Industrial Maintenance?
Grease fittings play a critical role in ensuring that grease is delivered precisely where it’s needed without contamination. Here’s why they matter:
- Contamination prevention: The built-in check valve blocks dirt, moisture, and debris.
- Equipment longevity: Ensures bearings and moving parts are properly lubricated.
- Efficiency: Reduces friction, overheating, and energy loss.
- Safety: Remote fittings allow greasing without dismantling machinery or entering hazardous zones.
- Cost savings: Prevents expensive bearing failures and minimizes downtime.
For B2B buyers, selecting the right fitting type also affects total cost of ownership — the correct design can reduce lubrication time by up to 30% in heavy equipment operations.
How to Select the Right Grease Fitting
When choosing a grease fitting, consider the following criteria:
| Selection Factor | Recommendation |
| Accessibility | Straight for open areas, angled or remote for tight spaces |
| Lubrication Frequency | Button-head for frequent, high-volume greasing |
| Pressure Rating | Check manufacturer specs; heavy-duty systems need high-pressure fittings |
| Environmental Conditions | Use stainless steel or brass for corrosive environments |
| Space Constraints | Flush fittings where clearance is minimal |
| Thread Type | Match regional or OEM standards (SAE, NPT, Metric, BSPT) |
For example, in valve manufacturing, grease fittings used in actuator housings often differ from those used in sealing cavities. Selecting the right type ensures smooth valve operation, minimizes leakage, and prolongs seal life.
FAQ
What Is the Function of a Grease Fitting?
A grease fitting serves as a one-way valve that allows lubricant to enter a mechanical system under pressure while preventing contaminants or lubricant backflow.
Are All Grease Fittings the Same?
No. Grease fittings vary by shape (straight, angled, button-head, flush, remote), thread type, and material. Each is designed for specific space, pressure, and accessibility requirements.
How Often Should Grease Fittings Be Replaced?
Grease fittings rarely fail, but they should be inspected periodically for clogs, corrosion, or leakage. Replace any fitting that resists grease flow or no longer seals properly.
Can You Use Any Grease Gun with Any Fitting?
Most grease guns are compatible with standard Zerk fittings, but button-head and flush fittings require special couplers. Always confirm compatibility before servicing.
Conclusion
Grease fittings may appear small, but they play a big role in keeping industrial equipment running efficiently. Whether you’re maintaining instrumentation valves, bearings, or manifolds, selecting the right fitting type — straight, angled, button-head, flush, drive-type, or remote — ensures consistent lubrication, reduced wear, and extended equipment life.
For B2B suppliers like WalterValves, offering a complete range of grease fittings means more than just product variety; it’s about providing practical, maintenance-driven solutions that help customers avoid downtime and save costs.
Would you like to learn more about choosing or sourcing the right grease fittings for your equipment?
Leave a comment below, share your experiences, or contact us at info@waltervalves.com for expert support.